Technology
- Enhanced CLIP sequencing (eCLIP & Ribo-eCLIP)
- Circular RNA sequencing (circRNA-seq)
- RNA Synthesis
As RNA binding proteins (RBPs) play essential roles in cellular physiology by interacting with target RNAs, binding site identification by UV-crosslinking and immunoprecipitation (CLIP) of ribonucleoprotein complexes is critical to understanding RBP function. However, current CLIP protocols are technically demanding and yield low-complexity libraries with high experimental failure rates. We have developed an enhanced CLIP (eCLIP) protocol that decreases requisite amplification by ~1,000-fold, decreasing discarded PCR duplicate reads by ~60% while maintaining single-nucleotide binding resolution. By simplifying the generation of paired IgG and size-matched input controls, eCLIP improves specificity in the discovery of authentic binding sites.1,2,3
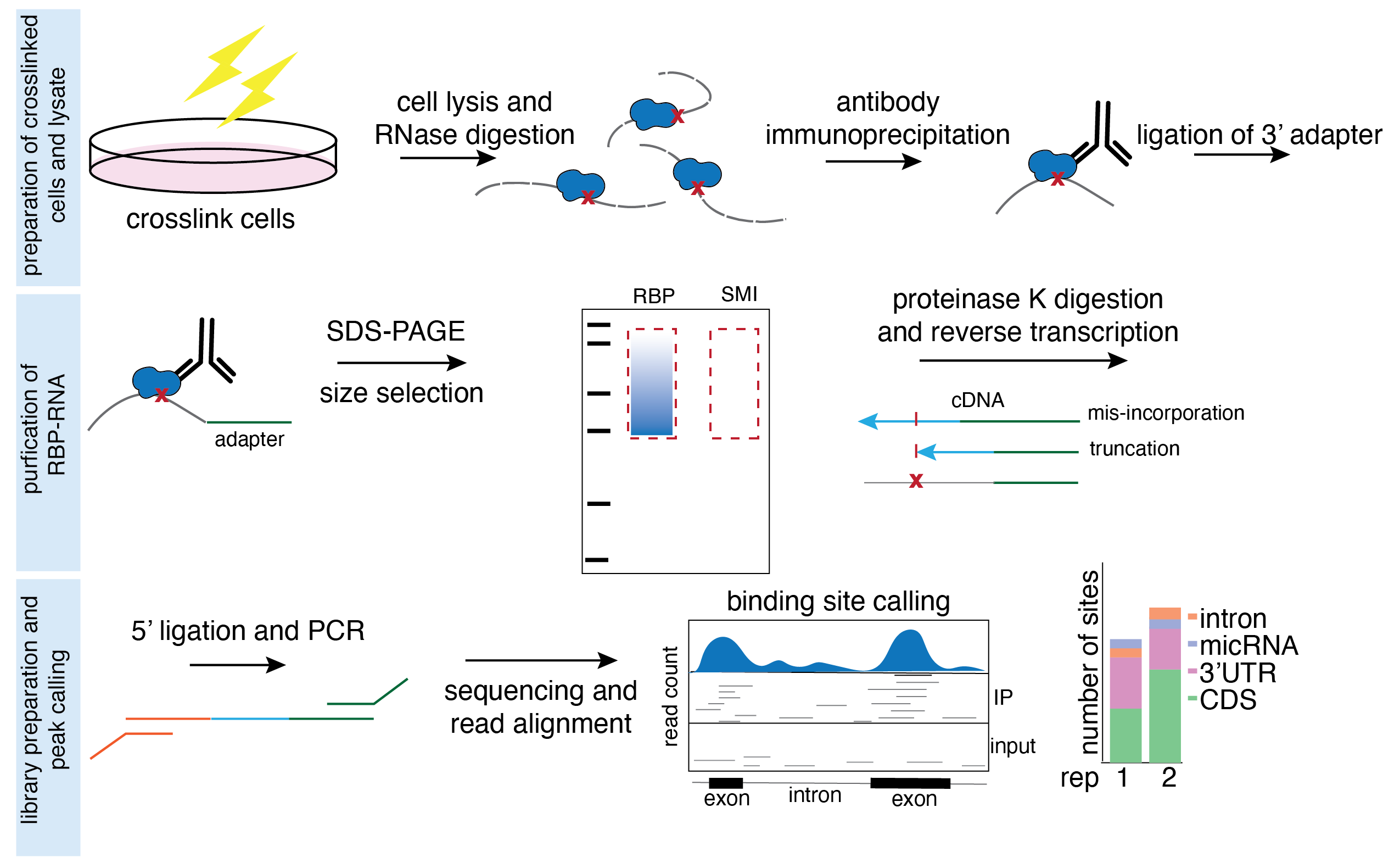
eCLIP is a powerful technique used to map RNA-binding protein (RBP) binding sites across the entire transcriptome. This technique has a wide range of applications that provide valuable insights into the regulation of target transcripts by RBPs. Below are some key applications of eCLIP:
Maps RBP binding sites and identifies RNA targets: eCLIP maps the binding sites of RBP on RNA molecules. Mapping the binding sites to specific sites within the transcript (5’UTR, splice sites, CDS etc.) gives insight into how an RBP regulates its target transcripts. Additionally, the identity of these target transcripts also informs what biological functions the RBP regulates.
Functional Annotation of Non-Coding RNAs: eCLIP can be used to study the binding of RBPs to non-coding RNAs, such as long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs). This sheds light on the regulatory networks involving these non-coding RNAs.
Disease Mechanisms: Researchers can use eCLIP to investigate how dysregulation of RBPs and their binding to RNA contribute to various diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and autoimmune conditions.
Drug Discovery and Development: Identifying RBP binding sites can aid in drug discovery by uncovering novel targets for small molecule drugs or RNA-based therapeutics. It can also be used to study the effects of RNA-targeted drugs on RBP-RNA interactions.
Comparative Analysis: eCLIP data can be compared across different cell types, tissues, or conditions to gain a comprehensive understanding of how RBP binding patterns vary in different biological contexts.
Functional Genomics: The integration of eCLIP datasets such as transcriptomics, RNA half-life, differential splicing, and proteomics can help pinpoint the function RBP has on its RNA targets.
Translation Regulation: Ribo-eCLIP data maps the ribosome-associated RNAs and the data can be used to analyze translation efficiency.